Diamond:
The Four C’s and Shape.
This short tutorial explains the Four C’s- Cut, Color, Clarity, and Carat weight – these are most important characteristics Goldman Diamond Exchange considers when buying a diamond.
Diamond Shape
As the name suggests, shape (round, princess, radiant, etc.) describes a diamond’s form, primarily as viewed from above. Since all diamond shapes are very different, unique characteristics determine quality for each shape.
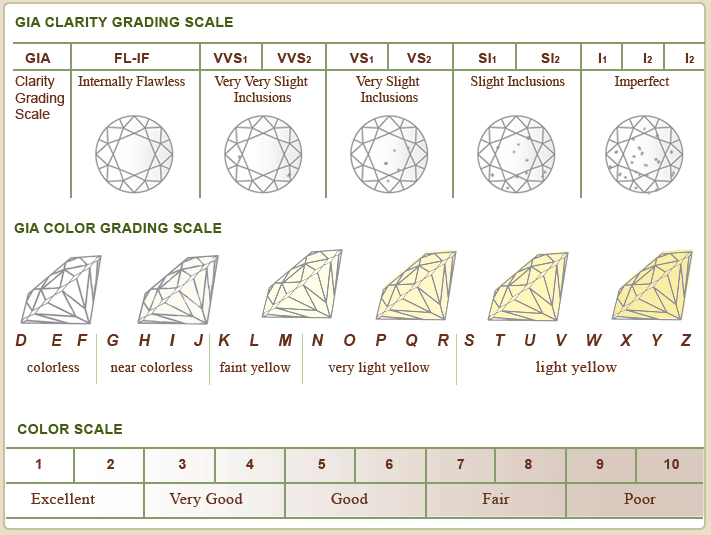
Diamond Clarity
Almost all diamonds have tiny imperfections. Diamonds with few or no imperfections receive the highest clarity grades. Basically there are two types of flaws: inclusions and blemishes. Inclusions refer to internal flaws and blemishes refer to surface flaws.
Diamond Cut
The cut of a diamond determines its brilliance. Put simply, the better a diamond is cut, the more sparkle it will have.
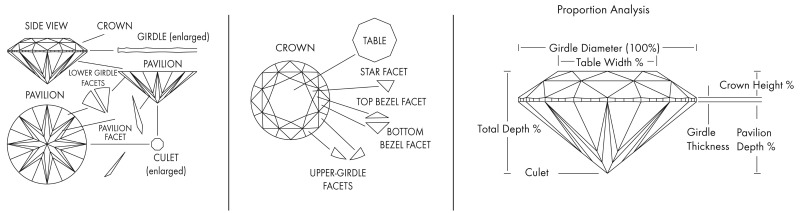
Diamond Anatomy
A diamond is comprised of five main components:
Table
• The largest facet of the diamond, which comprises the flat surface on the top of the stone, resembling a ‘table’.
Crown
• This is the top portion of the diamond, located above the girdle and extending below the table.
Girdle
• Forming the outer edge of the diamond, this is where the crown and the pavilion meet.
Pavilion
• Located at the bottom of the diamond, the pavilion bridges the girdle and the culet.
Culet
• The smallest facet of a diamond, the culet is located at the very bottom of the stone.
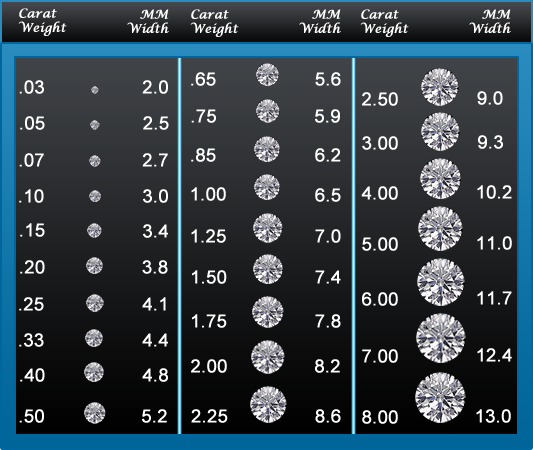
Diamond Carat Weight
This is the term with which people are most familiar, but bear in mind that carat is specifically a measure of a diamond’s weight. A carat (ct.) is the unit of measurement specifically used to describe the weight of a diamond (or other gemstones).
Diamond Color
A diamond’s color grade actually refers to the lack of color. In other words, diamonds that are white, containing little or no color, receive higher quality grades than those with visible color. The diamond color evaluation of most gem-quality diamonds is based on the absence of color. A chemically pure and structurally perfect diamond has no hue, like a drop of pure water, and consequently, a higher value.



Add a Comment